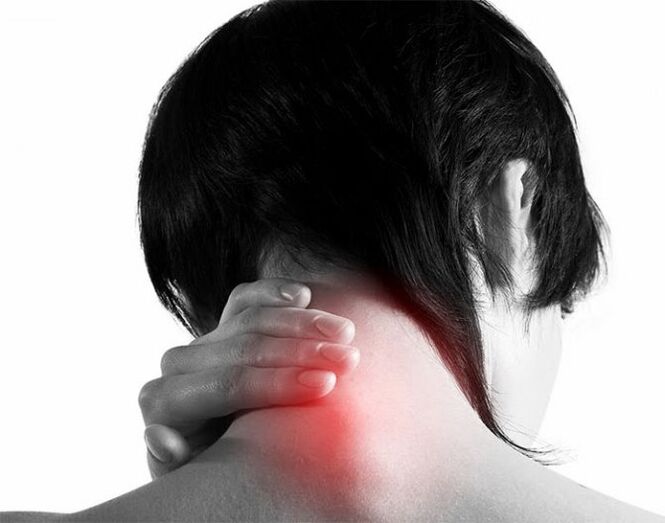
Osteochondrosis is a lesion of intervertebral discs of degenerative-dystrophic nature, and the cervical spine is the most sensitive part of the spine, which has an anatomically different structure of very close adjacent vertebrae and a weak muscular corset. Therefore, even with small additional loads on the neck, vertebral displacement can occur, leading to compression of blood vessels and nerves.
And since the vertebral arteries involved in the blood supply to the brain pass through holes in the transverse processes of the vertebrae in this section, squeezing the vertebrae in this section or squeezing the holes with overgrown osteophytes is fraught with very serious consequences.
What is it?
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a polyethiologically progressive disease manifested by degeneration of the intervertebral discs and dystrophy of the ligament apparatus of the spine.
Causes
The main causes and prerequisites for the occurrence of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are:
- Curvature of the spine, scoliosis.
- Stress, nervous tension negatively affect the general condition of the body, can cause cervical osteochondrosis.
- Delayed infectious diseases often become the root cause.
- Irregular, uncomfortable body position during sleep (for example, uncomfortable pillow).
- Congenital problems or the presence of hereditary diseases of the cervical spine.
- Poor posture in young and adolescent years.
- Overweight, obesity of varying degrees. Excess weight increases the load on the vertebrae and discs, which leads to degenerative processes.
- Back injuries that could have occurred during childhood or adolescence.
- Disorder of metabolic processes.
- Work related to physical work, which can cause diseases of the spine in various parts of it.
- Inactive lifestyle, inactive work, improper performance of any exercise.
For successful treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, it is first necessary to determine the cause, the preconditions that caused its development and remove them. Until recently, the disease occurred only in people older than 45 years. Now young people are exposed to it, the age range is 18-25 years.
Characteristics of the cervical spine
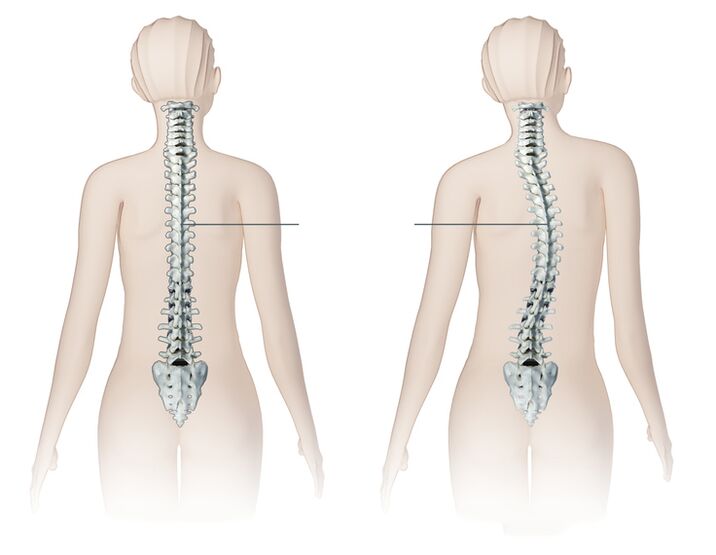
Consider how the cervical region differs from the rest of the spine and that in the process of developing osteochondrosis is a prerequisite for the development of these syndromes.
- There are important ganglia (nodes) of the autonomic nervous system in the cervical region.
- In the transverse processes of the vertebrae, there are holes that form a canal through which the spinal artery passes, which supplies the brain, brain, hearing organs, as well as the spinal nerve, with oxygen and nutrients. These are prerequisites for frequent pinching of arteries and nerves.
- The cervical spine is the most reliable. It is characterized by all kinds of movements completely. These are prerequisites for frequent violations and subluxations!
- The intervertebral foramen of the lower three vertebrae are not round but triangular. These are prerequisites for the disruption of nerve roots by bone growths, which occur in osteochondrosis.
- Intervertebral discs are not located between the vertebral bodies along their entire length. In the front, instead, there are protruding edges of the vertebrae that are interconnected by joints.
Here are the key features that we will build on, analyzing the symptoms and complications of osteochondrosis.
Stages of development
The degree of osteochondrosis is determined by the clinical picture and the patient's complaints. The term degree should not be confused with the stages of osteochondrosis. The phases will be discussed below.
- First degree. clinical manifestations are minimal, the patient may complain of low-intensity cervical spine pain, may worsen when turning the head. Physical examination may show mild neck muscle tension.
- Second degree. the patient is worried about pain in the cervical spine, its intensity is much higher, the pain can be irradiating in the shoulder, in the arm. Painful sensations increase when tilting and turning the head. The patient may notice a decrease in performance, weakness, headache.
- Third degree. the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis intensify, the pain becomes constant by radiation to the arm or shoulder. Numbness or weakness appears in the muscles of the arm while herniated discs are forming (see symptoms of lumbar spine hernia). Examination reveals limited mobility of the cervical spine, pain on palpation of the cervical spine.
- Fourth degree. there is a complete destruction of the intervertebral disc and its replacement by connective tissue. Dizziness intensifies, tinnitus appears, coordination is disturbed.
Symptoms
The severity of the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis depends on the degree of destruction of the vertebral structures. Symptoms are aggravated by the growth of bone tissue by the formation of osteophytes, radicular syndrome (radicular pain when the nerve is compressed), intervertebral hernia (protrusion of the disc into the spinal canal).
The first signs of the disease are periodic headaches in the back of the head, neck pain, crunch and clicks in the vertebrae when turning the head, and sometimes slight tingling in the shoulders. Over time, the symptoms increase and the intensity of the pain increases.
Pain syndrome is the main manifestation of osteochondrosis. Neck pain can be dull, constant or sharp with lumbago below the nape of the neck when turning the head. The entire cervical region or the projection area of the modified vertebra, as well as the collarbone, shoulder, shoulder blade, and heart area, can ache. Restriction of head movement due to pain often occurs in the morning after sleeping in an uncomfortable position.
The disease leads to compression of the roots of the peripheral nerves (radicular syndrome) and causes pain during their nervousness. Perhaps numbness of the hands or fingers, impaired sensitivity of certain areas of the skin innervating the pinched nerve.
According to some characteristic symptoms, it can be assumed which vertebrae are affected:
- C1 - violation of sensitivity in the occipital region;
- C2 - pain in the occipital and parietal region;
- C3 - decreased sensitivity and pain in the middle of the neck where the spinal nerve is damaged, possible damage to the sensitivity of the tongue, speech impairment due to loss of control over the tongue;
- C4 - impaired sensitivity and pain in the shoulder-scapular region, decreased tone of the muscles of the head and neck, possible respiratory disorders, pain in the liver and heart;
- C5 - pain and impaired sensitivity on the outer surface of the shoulder;
- C6 - pain that spreads from the neck to the shoulder blade, forearm, outer surface of the shoulder, radial surface of the forearm to the thumb;
- C7 - pain that spreads from the neck to the shoulder blade, back of the shoulder, forearm to II - IV fingers of the hand, impaired sensitivity in this area.
- C8 - pain and noticeable damage spread from the neck to the shoulders, forearms to the little finger.
Clicks or crunches during neck movements almost always accompany cervical osteochondrosis, observed in every patient. Crunching occurs during a sharp turn of the head or throwing backwards.
Syndromes due to cervical osteochondrosis
The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are grouped, called syndromes. Their presence and severity may indicate pathology of the cervical spine with a certain localization.
Set of common syndromes:
- Vegetative-dystonic syndrome. Subluxation of the first vertebral column with displacement may lead to the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia. VSD is not a definitive diagnosis because it has no pronounced symptoms. There may be neurological signs, symptoms of impaired cerebral blood flow, jumps in intracranial pressure, muscle cramps. As a result, the patient's complaints are reduced to dizziness, decreased visual acuity, loss of consciousness, headache and nausea.
- Irritating and reflexive. Burning and sharp pain in the back of the head and neck, sometimes with a return to the chest and shoulder, occurring at the time of changing the position of the head and neck, with sneezing and a sharp turn of the head.
- Radicular. Otherwise called cervical radiculitis, it combines symptoms associated with injury to the nerve roots of the cervical spine. It is characterized by "chills" in the affected area, tingling in the fingers, forearms, pasty skin, spreading to certain fingers.
- Hearty. Almost the same picture with angina pectoris often leads to misdiagnosis and treatment. The syndrome occurs due to irritation of the phrenic nerve receptors, partially affecting the pericardium and the large chest muscle. Therefore, spasms in the heart area are more reflexive, like a response to irritation of the cervical nerves.
- Vertebral artery syndrome. It develops directly by compressing the artery itself, as well as by irritating the plexus of the sympathetic nerve that is around it. Pain in this pathology is a burning or pulsation in the occipital region and extends to the temples, adrenal arches, crown. It occurs on both sides. Patients usually associate worsening with the condition after sleeping in an unphysiological position, traveling in transport, walking. Severe symptoms may include hearing loss, dizziness, tinnitus, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, and high blood pressure.
Nonspecificity and the large number of different symptoms that accompany this disease make diagnosis and further treatment difficult, as some of them can be a sign of completely different diseases.
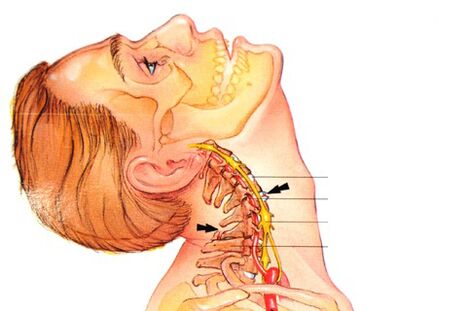
Diagnosis
As with any diagnosis in medicine, the diagnosis of osteochondrosis is established based on patient complaints, medical history, clinical examination, and assisted research methods. Radiography of the cervical spine is performed in frontal and lateral projections, if necessary in special positions (with open mouth). At the same time, experts are interested in the height of the intervertebral discs, the presence of osteophytes.
Modern research methods use NMR and CT studies, which enable the most accurate verification of the diagnosis. In addition to the above methods of additional research, you may need to consult related specialists (cardiologist, ophthalmologist, neurosurgeon), and an examination by a neurologist is simply vital. The neurologist is engaged in the treatment of osteochondrosis, so, after examining the patient, he will prescribe the necessary minimum examination at his own discretion.
How to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
Complex treatment of cervical osteochondrosis can include the following traditional and non-traditional methods: drug treatment, massage, acupressure, manual therapy, physiotherapy, acupuncture, homeopathy, folk remedies, etc.
The main treatment regimen for osteochondrosis is the same for all localizations of this disease:
- You need to relieve the pain first.
- Then the swelling will be removed.
- At this stage, it is necessary to normalize blood circulation.
- Strengthening muscle corsets.
- Improving nutrition and tissue regeneration.
The list of drugs and medications for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis at home is very extensive:
- Anti-inflammatory (steroid). These are hormonal drugs that relieve inflammation and thus eliminate pain. Tablets and ointments based on the substances hydrocortisone, prednisolone or dexamethasone are most often used for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- Analgesics (nonsteroidal pain relievers). They are usually prescribed in the form of tablets or capsules. It should be borne in mind that most of these drugs irritate the lining of the digestive tract. Among the modern drugs used to relieve pain in osteochondrosis;
- Muscle relaxants are drugs that relax muscle tone. They are used in surgery and orthopedics as aids to relieve pain. These drugs are administered parenterally, and therefore always under the supervision of a physician. There is an extensive list of contraindications;
- Chondroprotectors are preparations that contain substances that replace cartilage components - chondroitin, hyaluronic acid. In order to achieve a lasting positive effect, such drugs must be taken for a very long time;
- Ointments and gels for external use. This is the most affordable group of medicines for use at home. They are divided into relieving inflammation, warming and relieving pain. Such funds are often advertised. In cervical osteochondrosis, not all fats are effective, moreover, due to their availability, they are sometimes used unreasonably and without taking into account the peculiarities of pathogenesis.
- Vitamins. In osteochondrosis, vitamins are prescribed that have a beneficial effect on the peripheral nervous system and improve conduction. Water-soluble vitamins: B1, B6, B12, fat-soluble vitamins: A, C, D, E. In recent years, it has become increasingly common to prescribe combined preparations that contain both painkillers and vitamin components. An effective preparation consists of vitamin B based on pyridoxine and thiamine, as well as anesthetics.
Only a team of good professionals can choose the most appropriate therapy, which includes a neurologist, physiotherapist, massage therapist, surgeon and vertebral neurologist.
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy for cervical osteochondrosis should be carried out outside of acute exacerbation. The greatest efficiency of this technique is during the recovery period. There should be no discomfort or pain during the performance of the complex!
- Exercise # 1 Lying on your stomach, put your hands on the floor, lift your head and torso, your back should be straight. Stay in this position for 1-2 minutes. Slowly lower yourself to the floor. Repeat 2-3 times.
- Exercise number 2 Lying on your stomach, stretch your arms along your body, turn your head to the left, try to touch the floor with your ear, and then your head to the right. Repeat 6-7 times in each direction.
- Exercise No. 3 In a sitting position, as you inhale, lean forward and try to touch your chest with your head, then exhale, bend over, and tilt your head back. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Exercise # 4 While sitting, place your palms on your forehead, press your palms to your forehead, and your forehead to your palms. Continue this exercise for 30 seconds. Repeat 2-3 times.
- Exercise number 5 Slowly rotate your head first in one direction and then in the other. 10 rotations in each direction. Watch out for dizziness. When it appears, the exercise stops.

Mass therapy
The massage can be performed at home, but very carefully so as not to aggravate and harm the patient. The patient should take a lying position, put his forehead on his hands and stretch his chin towards his chest. In this case, the neck muscles should be completely relaxed.
- Stroking. The massage should be started with these movements: stroking the collar zone in the direction from the lymph to the supraclavicular and axillary nodes. Then apply straight and comb strokes.
- Push-ups. To perform push-ups, the masseur puts his hand over the neck (index and thumb should be together) and moves down the spine. Push-ups can also be performed from the edge of the palm to the shoulder joints.
- Trituration. Rubbing is done to warm up the muscles, relax and improve blood flow in the area. The massage should start from the bottom of the skull, performing circular and rectilinear movements with the fingers. You can also perform sawing movements with your palms parallel to the ribs.
- Kneading. Kneading should be performed on the neck in a circular motion.
- Vibration. The massage ends with shocks and vibrations, which are performed with the help of shaking and beating.
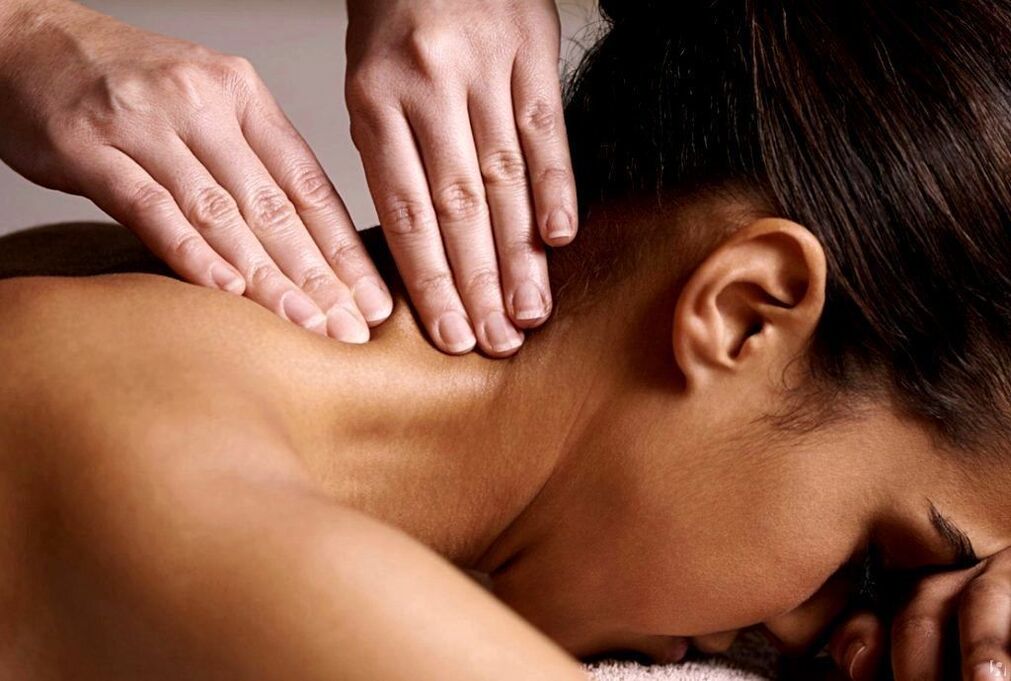

Massage is necessary to strengthen muscle tone and relieve pain. Depending on the stage of osteochondrosis, a massage technique is chosen. However, while doing neck massage, experts use all the techniques of classical massage: rubbing, smoothing, kneading, etc. In cases where the patient hurts in the neck area on one side only, the massage begins in the healthy part of the neck, gradually moving to the part of the collar where strong painful sensations occur.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy helps to cope with acute and chronic pain, also increases the range of motion and improves posture well. The main methods of manual therapy of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
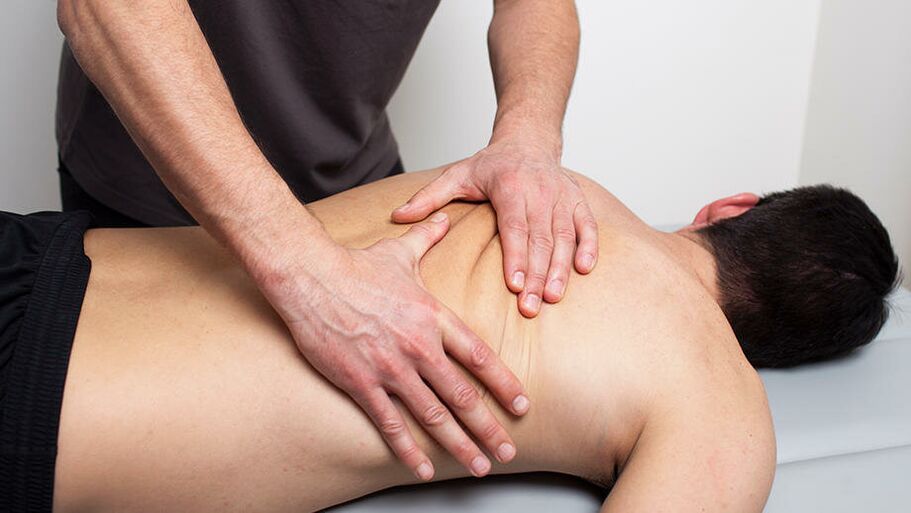
- Relaxing and segmental massage. It is used to warm up muscles and relieve tension.
- Mobilization. Effects aimed at restoring joint function. by the stretching method.
- Manipulation. Sharp thrust directed at the patient's pathological areas. The procedure is followed by a characteristic crunch (return of the joint to a normal position).
A specialist in manual therapy should be fluent in these techniques. Otherwise, any mistake can lead to injury.
Orthopedic pillows
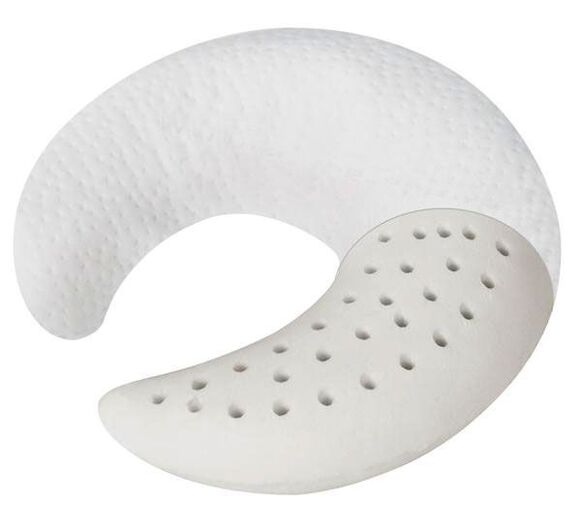

Orthopedic sleeping pillows are an effective preventative measure. In many cases, osteochondrosis is exacerbated by additional compression of the cervical artery and nerve roots while sleeping on an uncomfortable pillow. The orthopedic product ensures a uniform horizontal position of the person during sleep and thus guarantees a physiologically adequate blood supply to the brain.
When choosing a pillow, the individual anatomical features of the person should be taken into account and related to the volume and characteristics of the filler. Properly chosen pillow brings tangible benefits for a patient with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures for cervical osteochondrosis:
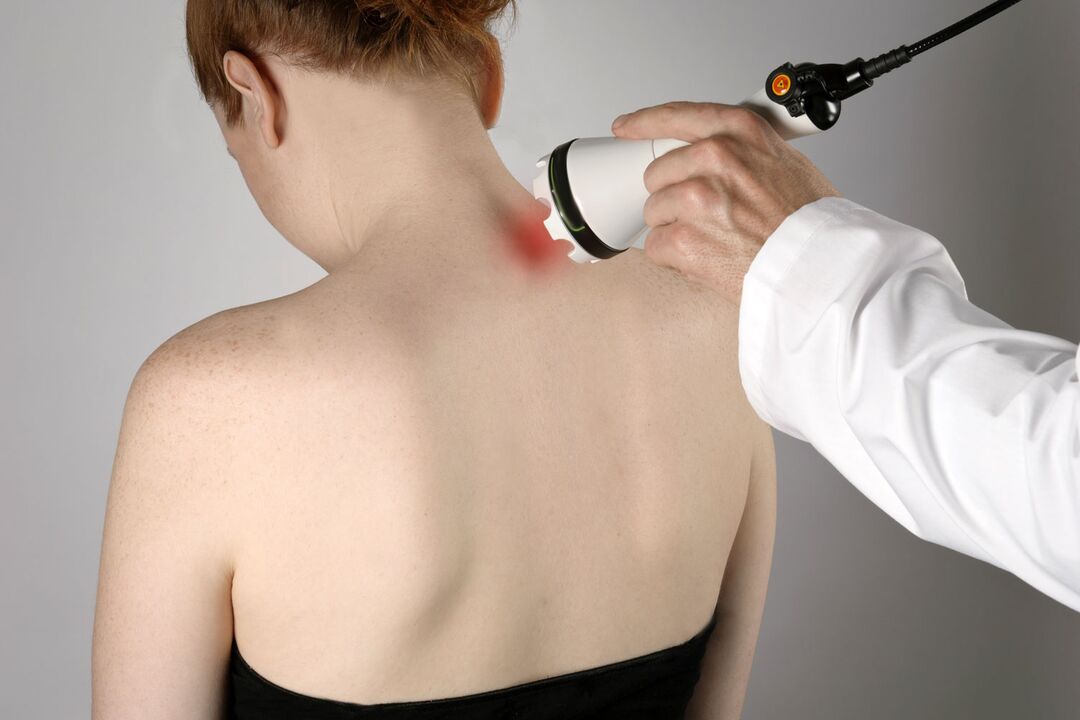
- Electrophoresis. It should be used with painkillers (anesthetics), which are injected under the skin with electronic impulses.
- Ultrasound. It has a beneficial effect on metabolic processes in the tissues of the cervical spine, due to which the swelling is removed and the pain disappears.
- Magnetotherapy. A safe method of treatment that consists of exposing damaged cells to a low frequency magnetic field. It gives an analgesic effect, acts as an anti-inflammatory agent
- Laser therapy. Improves blood circulation in the affected area, relieves tissue swelling, pain.
Physiotherapy procedures have a beneficial effect on the discs and vertebrae in cervical osteochondrosis. Combined with medication, combined treatment helps eliminate the symptoms of the disease. The procedures are performed in a hospital or specialized clinics. Before starting the course you need to consult a doctor, determine the duration of physiotherapy, the type. Transmission during exacerbations is strictly forbidden.
Shants Collar
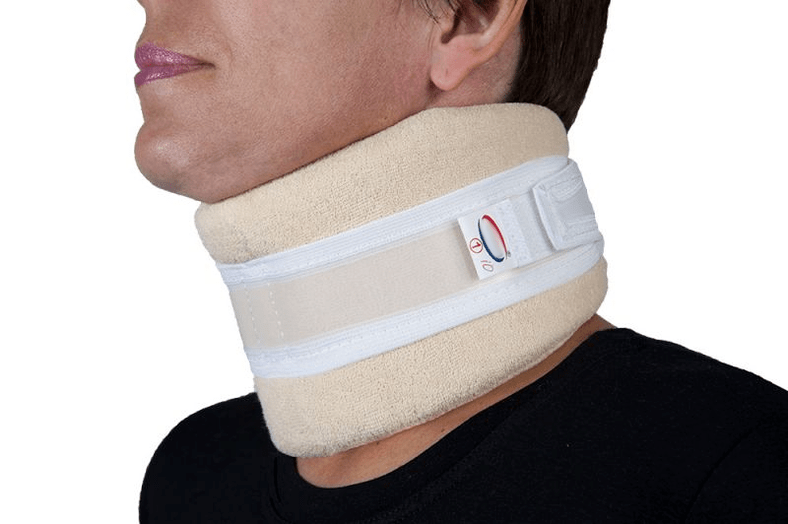
The Shants necklace is a soft and comfortable device that fastens with the back velcro straps and is used for cervical osteochondrosis. But not for treatment, but for temporary relaxation and alleviation of fatigue. It cannot be worn without stripping, otherwise the neck muscles will stop working and soon atrophy. If the Shants collar is chosen correctly, the patient feels comfortable and protected.
The necklace is chosen strictly according to size in a pharmacy or orthopedic store. Better in the store, because the people who work there, as a rule, know their business and product characteristics quite well, which means that they can help in each specific case.
Folk remedies
If the pain from osteochondrosis of the spine becomes unbearable and regular, you will agree to everything to stop it, and here the traditional complex treatment will be successfully supplemented with alternative methods.
- insist on celery root (5 grams per 1 liter of boiling water) 4 hours, drink a tablespoon before each meal;
- honey compress, for which we take 2 tsp. honey and 1 tablet of mummy. The components are heated in a water bath, spread on a cloth and applied at night to the cervical region, ie the neck;
- in case of acute pain horseradish growing in the ground helps me. I just wash his leaf, pour boiling water over it, cool it down a bit, apply it on his neck and wrap it in a thin scarf for the night - in the morning you can already live and work;
- insist on chamomile flowers in vegetable oil for two days, heating to boiling (for 500 ml of oil you need 30 grams of the plant), rub into painful areas;
- Honey-potato compress also helps, because the root must be grated and mixed with honey in the same amount, applied to the large neck at night, regularly, at least once a week.
Prophylaxis
As usual, proper prophylaxis will help avoid osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, but, of course, all physical exercise must be used regularly, because "periodic" exercises will not be of much use.
It remains to remember simple rules:
- eat more foods high in calcium and magnesium. These are fish, peas, legumes, nuts, cheese, herbs, but it is better to refrain from sugar, flour, smoked, spicy foods.
- doing sports regularly, especially swimming, water aerobics, stretching gymnastics and spine flexibility is also perfect for preventing osteochondrosis that can be exercised at home.
- during sedentary work, at least several times a day, perform a special set of exercises, an example of which is in the video.
- choose a good orthopedic mattress and pillow that is ideal for the neck, supporting the head in sleep in the correct anatomical position (yes, your favorite huge lower pillows will not disappear with spine problems! ).
If you already have such a diagnosis, then the patient should spare the spine, as follows:
- Be very careful with lifting and carrying weights, it’s better to go to the store twice than to pull heavy bags in both hands, incredibly straining your neck and shoulder girdle;
- Do not cool down, avoid drafts and the flow of cold air from the air conditioner (some people like to cool down on a hot day, standing with their backs to the fan);
- When you bend your body forward - remember osteochondrosis;
- Avoid local overheating of the muscles, which can happen to those who like an excessively hot bath;
- Remember to occasionally detach yourself from the monitor, change body position, do not sit for hours or even days;
- Rest your neck, for which you need to buy a Shants necklace;
- If possible, if the condition of the cardiovascular system allows, take a steam bath.
In conclusion, I would like to say that a child at risk of osteochondrosis (father and mother already have it) and an adult who acquired the disease during their lifetime are simply obliged to take preventive measures so as not to become disabled and not be on the operating table, because this operation is quitesevere and requires long-term rehabilitation. In addition, this is not always possible, because there are inoperable cases, so it is better to protect health from small feet, as long as the discs are intact and unnecessary growths do not constrict blood vessels.